Impact of nanoscale morphology on charge carrier delocalization and mobility in an organic semiconductor
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202104852

THE LONDON CENTRE FOR THE THEORY & SIMULATION OF MATERIALS & MOLECULES

THE LONDON CENTRE FOR THE THEORY & SIMULATION OF MATERIALS & MOLECULES
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202104852
Researchers from the University of Cambridge, University College London, Imperial College London and Charles University in Prague have developed a powerful machine learning based procedure for molecular simulations of complex systems. The results, reported in the journal PNAS, open the…
Molecular cages have potential as enzyme-mimics and in applications such as catalysis, drug-delivery and sensing. Recently, chemists have attempted to introduce more complexity into their structures in an attempt to emulate Nature’s success with proteins and enzymes. However, it can…
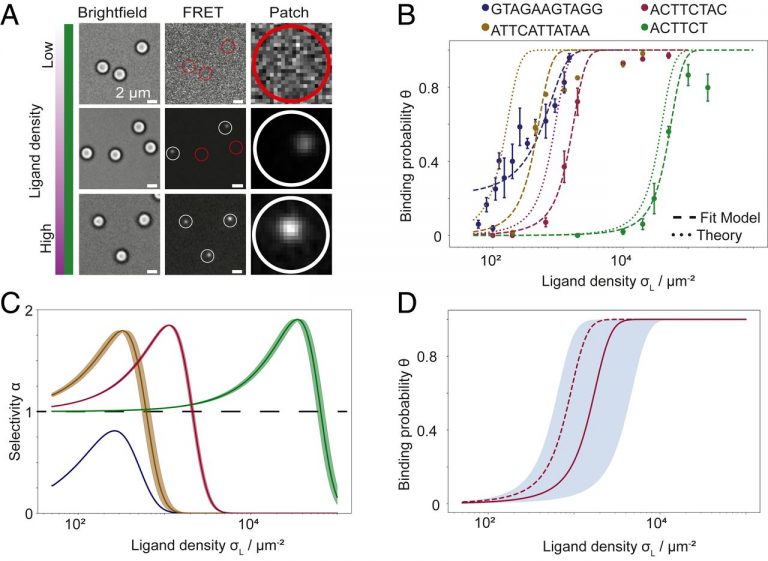
https://www.pnas.org/content/118/36/e2106036118/tab-article-info
In the last decade researchers have realised that simply shaking a collection of quantum particles can give rise to new phases of matter without any counterparts in undriven equilibrium systems. However, most of these are rather delicate and require a…
Today’s quantum computers are small and noisy. Hybrid quantum-classical algorithms aim to make use of these limited devices by pairing them with classical computing and assigning specialized tasks to the quantum hardware (e.g. measuring the energy expectation value of a…

Perovskite-inspired materials aim to replicate the optical and electronic performance of the famous lead-halide perovskites, while eliminating issues with stability and toxicity. In this work, we focused on an emerging material in the class of mixed-metal chalcohalides; Sn2SbS2I3, which recently…
This work was part of a long-term collaboration between the groups of Charles Sykes (Tufts University), Angelos Michaelides (former TYC Director and Professor at UCL, now at the University of Cambridge) and Michail Stamatakis (UCL). Notably, this collaboration was fostered…
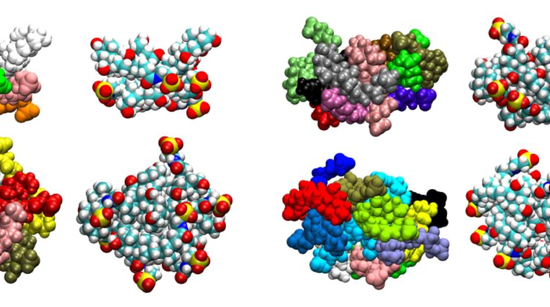
Bile salts (BS) are biosurfactants released into the small intestine, which play key and contrasting roles in lipid digestion: they adsorb at interfaces and promote the adsorption of digestive enzymes onto fat droplets, while they also remove lipolysis products from that…
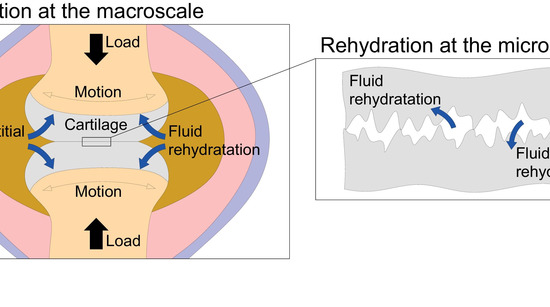
Carmine Putignano, David Burris, Axel Moore, Daniele Dini In this study we have provided an innovative theoretical formulation, corroborated by detailed experiments, which for the first time sheds the light on the hydrodynamic origins of rehydration in cartilage tissues. When…