A deep learning method to predict ice formation outperforms human scientists
Accurate prediction of ice nucleation from room temperature water

THE LONDON CENTRE FOR THE THEORY & SIMULATION OF MATERIALS & MOLECULES

THE LONDON CENTRE FOR THE THEORY & SIMULATION OF MATERIALS & MOLECULES
Accurate prediction of ice nucleation from room temperature water
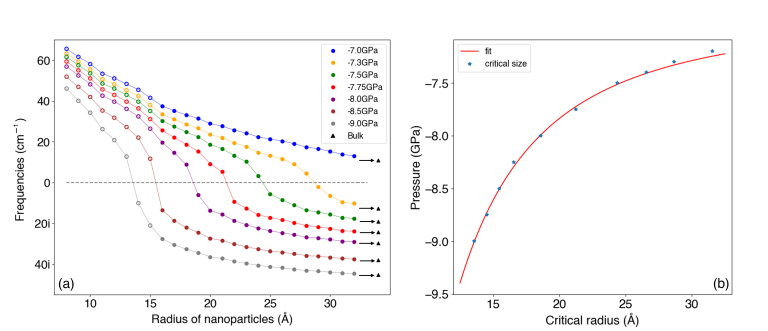
Much of the interest in nanomaterials derives from their size-dependent structural and functional properties, including their behavior under pressure. To exploit the relationship between size and behavior under pressure, and thus tailor the properties of functional nanoparticles, a precise understanding…
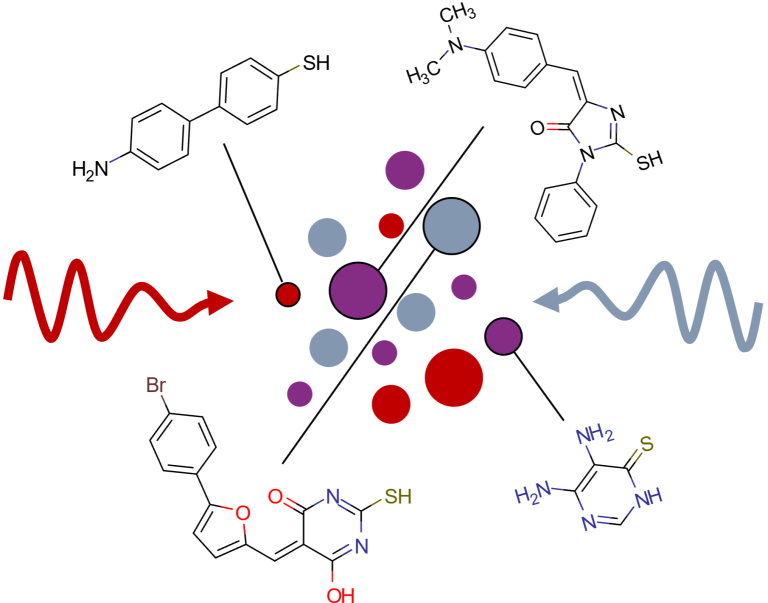
Surface-enhanced spectroscopy leverages the extreme enhancement of molecular signals in carefully engineered metallic nanostructures. There is great potential of surface-enhanced infrared absorption, Raman scattering, and vibrational sum-frequency generation for biosensing, security scanning, THz detection, or even remote control of chemical…
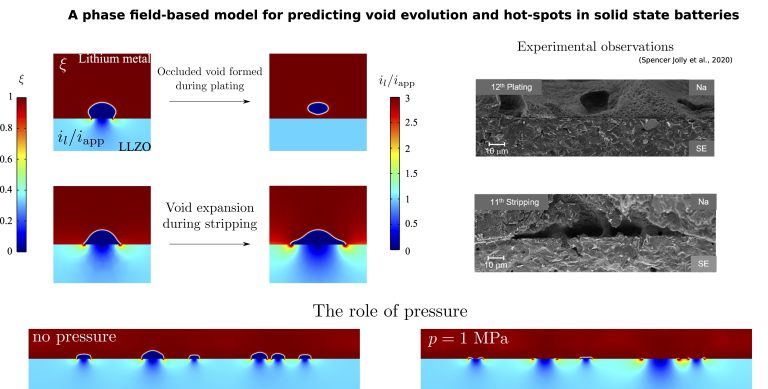
All-solid-state batteries are arguably the most promising development in energy storage technology. However, commercialisation is hindered by the formation of voids and dendrites at the interface between the Li metal anode and the solid electrolyte. In this work, a mechanistic…
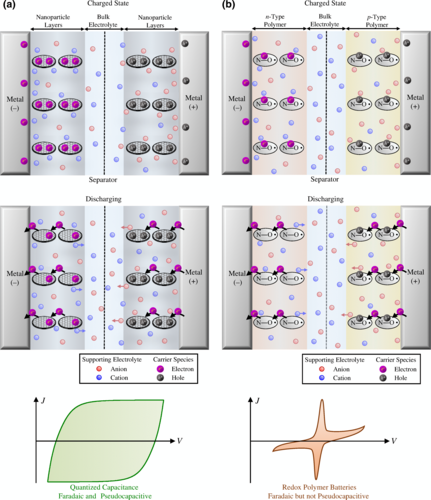
Pseudocapacitive components allow more charge to be stored by reactions on the surface of electrodes
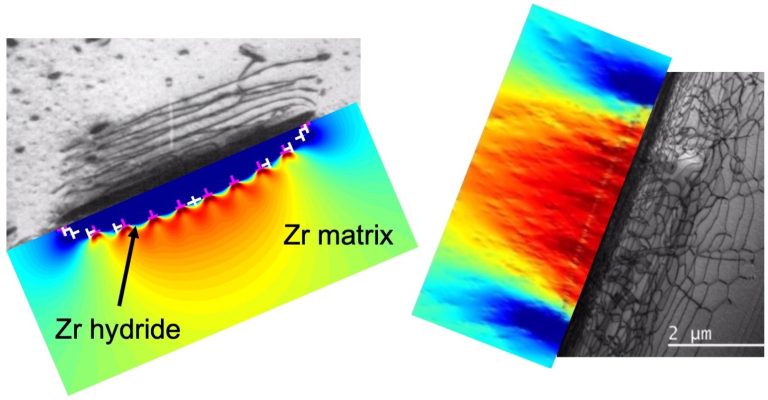
Nuclear fuel pellets are clad by thin zirconium tubes whose structural integrity is of paramount importance. The presence of the water coolant, however, provides hydrogen that reacts with zirconium to produce hydrides. Thermal cycles during normal reactor operations can lead…
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2022/cp/d2cp00752e
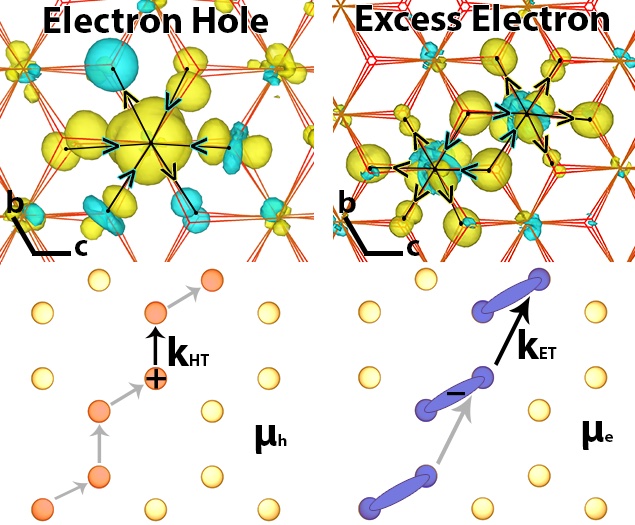
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.1c13507
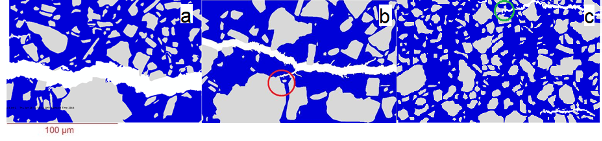
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S135983682200021X
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41566-021-00950-4